

You’re talking about the people who lowered a car from a rocket crane onto the surface of another planet, you can be thoughtfully critical, but their technical record has earned them a lot more than surface level dismissal.


You’re talking about the people who lowered a car from a rocket crane onto the surface of another planet, you can be thoughtfully critical, but their technical record has earned them a lot more than surface level dismissal.


deleted by creator


They better change that taskbar before releasing to consumers.
They somehow managed to combine the “take up the full width no matter what’s needed” mentality of Windows with the “show the user no useful information whatsoever” mentality of MacOS.


“This isn’t a meeting about the budget per se”
“This isn’t exactly a meeting about the budget”
If you finish those sentences, it becomes clear why per se is used:
“This isn’t a meeting about the budget per se, it’s a meeting about how much of the budget is spent on bits of string”
“This isn’t exactly a meeting about the budget, it’s a meeting about how much of the budget is spent on bits of string”
In this situation, using per se provides a more natural sentence flow because it links the first part of the sentence with the second. It’s also shorter and fewer syllables.
“Steve’s quite erudite.”
“Steve’s quite intellectual.”
I think intellectual might be a closer synonym, but intellectual often has more know-it-all connotations than erudite which seems to often refer to a more pure and cerebral quality.
“Tom and Jerry is a fun cartoon because of the juxtaposition of the relationship between cat and mouse.”
“Tom and Jerry is a fun cartoon because of the side by side oppositeness of the relationship between cat and mouse that is displayed”
For those to say precisely the same thing it would have to be more like the above which doesn’t really roll off the tongue.
“I don’t understand, can you elucidate that?”
“I don’t understand, can you explain?”
Elucidate just means to make something clear in general, explaining something usually inherently implies a linguistic, verbal, explanation, unless otherwise stated.
Honestly, these all seem like very reasonable words to me for the most part. I can understand not using them in some contexts, but for the most part, words exist for a reason, to describe something slightly differently, and it takes forever to talk and communicate if we only limit ourselves to the most basic unnuanced terms.


When people use industry specific jargon and acronyms with someone not in their industry.
It is a very simple rule of writing and communication. You never just use an acronym out of nowhere, you write it out in full the first time and explain the acronym, and then after that you can use it.
Artificial diamonds can be made with a High Temperature, High Pressure (HTHP) process, or a …
Doctors, military folk, lawyers, and technical people of all variety are often awful at just throwing out an acronym or technical term that you literally have no way of knowing.
Usually though, I don’t think it’s a conscious effort to sound smart. Sometimes, it’s just people who are used to talking only with their coworkers / inner circle and just aren’t thinking about the fact that you don’t have the same context, sometimes it’s people who are feeling nervous / insecure and are subconsciously using fancy terms to sound like they fit in, and sometimes it’s people using specific terminology to hide the fact that they don’t actually understand the concepts well enough to break them down further.


For each of these, what would you use instead?


Setting that aside, exploring space is not the same thing as building a company town for the world’s least mentally stable pregnancy fetishist oligarch in an unworldly cold desert where everyone is sure to die.
I would argue that the majority of sci-fi has predicted otherwise.


Yeah bud, there’s also these little shelters called caves.
The author of the article literally guffaws at the prospect of respinning a planet’s core when that’s not remotely how you would approach that problem.
It would be like writing an article saying “Come on, you believe in vaccines? What, you think a scientist can cut open your individual cells and put antibodies in each one? You really think they have tweezers that small? Get real dum dum.”


The scale of what you just described is really goofy.
The word you’re looking for is “big”. As in, it embiggens the noblest spirit.
I don’t think it’s feasible to protect a mars-diameter disc of massive magnets from damage by either normal objects traveling through the area or from some human engineered attack.
It’s also not possible to protect the ISS from either of those and yet it’s operated fine for 30 years. You do not need every little bit of it to be perfect, you just need to deflect enough solar wind that it allows Mars atmosphere to build back up which is what provides the real protection.
If you’re imagining the capacity to create such an emplacement, don’t you imagine that such phenomenal effort and wealth of resources would be better spent solving some terrestrial problem?
Like I said, we waste more resources than that all the time. I’d rather we didn’t build yachts and country clubs and private schools, yet we do. There’s no reason to not get started building that array, especially if it will take a while.
There’s a real difference between e-waste, which is mostly byproducts of the petroleum refining process with electronic components smeared liberally on, many of which rely on petroleum byproducts themselves and electromagnets, which are, at the scale you’re discussing, massive chunks of metals refined, shaped and organized into configurations that will create magnetic fields when dc is present.
That is not what e-waste is. E-waste primarily consists of silicon chips and the metal wires connecting them. Even the circuit boards themselves are primarily fibre glass, not petroleum.
And no, we wouldn’t be creating those using actual magnets, we’d be using electro magnets, which is just coils of wire connected to PV and logic chips.
I quite frankly flat out do not understand why people on the left are so against space exploration suddenly. You know that Elon Musk is not the only billionaire right? And you know virtually that all of them just sit on their wealth, and do nothing with it but wast on luxury lifestyles for themselves right? Yeah it would be better if billionaire’s did not exist, but as long as they do, why are you upset about their money going to space exploration as opposed to just yachts and $20,000 a night hotel stays?


No, not really. If we’re talking about colonizing a planet, building a bunch of magnets connected to solar panels is not going to be that big or expensive a part of it.
It’s also the kind of relatively cheap thing that takes a long time that we may as well get started now. I mean we churn out that much bullshit e-waste constantly for no reason, if we were more focused / more billionaire’s money went to that, you might actually be able to get it done.


deleted by creator


The rub there is that it’s 1-2 Tesla’s over the whole cross sectional area of Mars (I believe).
It’s not that hard to make a 2 Tesla magnet, but the most powerful electromagnet we’ve ever made is only 45 Tesla’s and even that only produces a 2 Tesla strong field out to 2.8m. So you might be looking at a Mars diameter worth of small magnets.


Solar panels would be my guess, though you can always build a space based nuclear reactor if you can refuel it and get rid of its waste.
It would certainly need a lot more to figure out an actual feasible plan, but I don’t think there’s anything fundamentally impossible about doing it with today’s technology, let alone the future’s.


This is a pretty embarassing way to open this article:
Mars does not have a magnetosphere. Any discussion of humans ever settling the red planet can stop right there, but of course it never does. Do you have a low-cost plan for, uh, creating a gigantic active dynamo at Mars’s dead core? No? Well. It’s fine. I’m sure you have some other workable, sustainable plan for shielding live Mars inhabitants from deadly solar and cosmic radiation, forever. No? Huh. Well then let’s discuss something else equally realistic, like your plan to build a condo complex in Middle Earth.
NASA legitimately has a plan for this, and no it’s not crazy, and no it doesn’t involve restarting the core of a planet:
https://phys.org/news/2017-03-nasa-magnetic-shield-mars-atmosphere.html
You just put a giant magnet in space at Mars’ L1 Lagrange point (the orbital point that is stable between Mars and the sun), and then it will block the solar wind that strips Mars’ atmosphere.
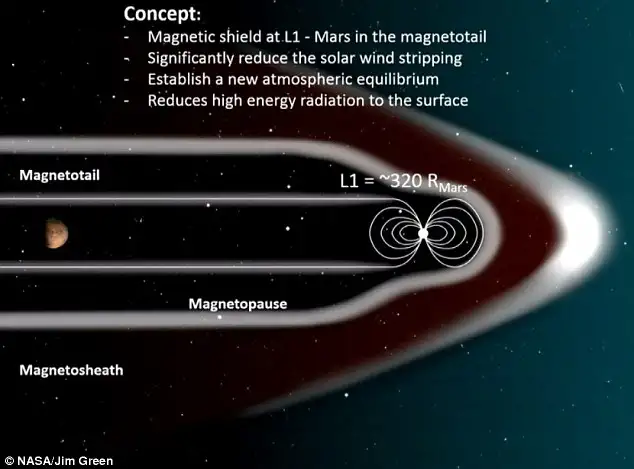
Otherwise cosmic rays etc are blocked and interrupted by the atmosphere, not the magnetosphere.
The confident dismissiveness of the author’s tone on a subject that they are (clearly) not an expert in, let alone took the time to google, says all you really need to know about how much you should listen to them.


I’m not google, you can figure this out for yourself:
https://arstechnica.com/cars/2023/12/human-drivers-crash-a-lot-more-than-waymos-software-data-shows/


Look up Waymo, then stop going on long winded rants about things when you don’t even have a basic grasp of the current state of the technology.
Jesus Christ.


you are literally doing what i mean when i say you are making assumptions with no evidence. there is, again, no reason to believe that “driving more efficiently” will result from mass-adoption of automated vehicles–and even granting they do, your assumption that this wouldn’t be gobbled up by induced demand is intuitively disprovable. even the argumentation here parallels other cases where induced demand happens! “build[ing] new roads or widen[ing] existing ones” is a measure that is almost always justified by an underlying belief that we need to improve efficiency and productivity in existing traffic flows,[^1] and obviously traffic flow does not improve in such cases.
I’m doing nothing other than questioning where the induced demand is coming from. What is inducing if not increased efficiency?
The whole point of induced demand in highways is that when you add capacity in the form of lanes it induces demand. So if our highways are already full and if that capacity isn’t coming from increased EV efficiency then where is it coming from? If there’s no increase in road capacity then what is inducing demand?
but granting that you’re correct on all of that somehow: more efficiency (and less congestion) would be worse than inducing demand. “efficiency” in the case of traffic means more traffic flow at faster speeds, which is less safe for everyone—not more.[^2] in general: people drive faster, more recklessly, and less attentively when you give them more space to work with (especially on open roadways with no calming measures like freeways, which are the sorts of roads autonomous vehicles seem to do best on). there is no reason to believe they would do this better in an autonomous vehicle, which if anything incentivizes many of those behaviors by giving people a false sense of security (in part because of advertising and overhyping to that end!).
You are describing how humans drive, not AVs. AVs always obey the speed limit and traffic calming signs.
you asserted these as “other secondary effects to AVs”–i’m not sure why you would do that and then be surprised when people challenge your assertion. but i’m glad we agree: these don’t exist, and they’re not benefits of mass adoption nor would they likely occur in a mass adoption scenario.
We haven’t agreed on anything,I said I was open to your reasoning as to why those effects wouldn’t happen, then you didn’t provide any.
the vast majority of road safety is a product of engineering and not a product of human driving ability, what car you drive or its capabilities, or other variables of that nature. almost all of the problems with, for example, American roadways are design problems that incentivize unsafe behaviors in the first place (and as a result inform everything from the ubiquity of speeding to downstream consumer preferences in cars). to put it bluntly: you cannot and will not fix road safety through automated vehicles, doubly so with your specific touted advantages in this conversation.
You think you can eliminate all accidents through road design?
You are literally ignoring every single accident caused by distracted driving, impatient driving, impaired driving, tired driving etc.
Yeah, road design in America should be better, AVs should still also replace crappy wreckless humans. Those two ideas are not mutually exclusive.


this is at obvious odds with the current state of self-driving technology itself–which is (as i noted in the other comment) subject to routine overhyping and also has rather minimal oversight and regulation generally
All cool tech things are overhyped. If you judgement for whether or not a technology is going to be useful is “if it sounds at all overhyped then it will flop” then you would never predict any technology would change the world ever.
And no, quite frankly those assertions are objectively false. Waymo and Cruise’s driverless programs are both monitored by the DMV which is why they revoked Cruise’s license when they found them hiding crash data. Waymo has never been found to do so or even accused of doing so. Notice that in the lawsuit you linked, Waymo was happy to publish accident and safety data but did not want to publish data about how it’s vehicles handle edge cases, which would give their rivals information on how they operate, and the courts agreed with them.
https://arstechnica.com/cars/2023/12/human-drivers-crash-a-lot-more-than-waymos-software-data-shows/
Since their inception, Waymo vehicles have driven 5.3 million driverless miles in Phoenix, 1.8 million driverless miles in San Francisco, and a few thousand driverless miles in Los Angeles through the end of October 2023. And during all those miles, there were three crashes serious enough to cause injuries:
In July, a Waymo in Tempe, Arizona, braked to avoid hitting a downed branch, leading to a three-car pileup. A Waymo passenger was not wearing a seatbelt (they were sitting on the buckled seatbelt instead) and sustained injuries that Waymo described as minor. In August, a Waymo at an intersection “began to proceed forward” but then “slowed to a stop” and was hit from behind by an SUV. The SUV left the scene without exchanging information, and a Waymo passenger reported minor injuries. In October, a Waymo vehicle in Chandler, Arizona, was traveling in the left lane when it detected another vehicle approaching from behind at high speed. The Waymo tried to accelerate to avoid a collision but got hit from behind. Again, there was an injury, but Waymo described it as minor. The two Arizona injuries over 5.3 million miles works out to 0.38 injuries per million vehicle miles. One San Francisco injury over 1.75 million miles equals 0.57 injuries per million vehicle miles. An important question is whether that’s more or less than you’d expect from a human-driven vehicle.
After making certain adjustments—including the fact that driverless Waymo vehicles do not travel on freeways—Waymo calculates that comparable human drivers reported 1.29 injury crashes per million miles in Phoenix and 3.79 injury crashes per million miles in San Francisco. In other words, human drivers get into injury crashes three times as often as Waymo in the Phoenix area and six times as often in San Francisco.
Waymo argues that these figures actually understate the gap because human drivers don’t report all crashes. Independent studies have estimated that about a third of injury crashes go unreported. After adjusting for these and other reporting biases, Waymo estimates that human-driven vehicles actually get into five times as many injury crashes in Phoenix and nine times as many in San Francisco.
To help evaluate the study, I talked to David Zuby, the chief research officer at the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety. The IIHS is a well-respected nonprofit that is funded by the insurance industry, which has a strong interest in promoting automotive safety.
While Zuby had some quibbles with some details of Waymo’s methodology, he was generally positive about the study. Zuby agrees with Waymo that human drivers underreport crashes relative to Waymo. But it’s hard to estimate this underreporting rate with any precision. Ultimately, Zuby believes that the true rate of crashes for human-driven vehicles lies somewhere between Waymo’s adjusted and unadjusted figures.


they can. induced demand is omnipresent in basically all vehicular infrastructure and vehicular improvements and there’s no reason to think this would differ with autonomous vehicles
Yes, I have no doubt there would be induced demand, but that extra demand wouldn’t be at the cost of anything. Induced demand is a problem when we, for instance, build new roads or widen existing ones, because then more people drive and they clog up the same as they were before. That’s a bad thing because the cost of adding this capacity is that we have to tear down nature and existing city to add lanes, and then we have more capacity that sits at a standstill leading to more emissions.
But if AVs add more capacity to our roads, that will be entirely because they are driving more efficiently. We’ll have the same amount of cars on the road at any given time, they’ll just be moving faster on average rather than idling in traffic jams made by humans. Which means that there will be only relatively minor emissions increases during peak times, fewer emissions emitted during non peak, and we won’t be tearing anything down to build more giant highways.
okay but: literally none of this follows from mass-adoption of autonomous vehicles. this is a logical leap you are making with no supporting evidence—there is, and i cannot stress this enough, no evidence that if mass-adoption occurs any of this will follow
You’re asking for something that does not exist. How am I supposed to provide you evidence proving what the results of mass adoption of AVs will be when there has never been a mass adoption of AVs.
and in general the technology is subject to far more fabulism and exaggeration (like this!) than legitimate technological advancement or improvement of society.
Again, it’s never actually been rolled out on a mass scale. It’s a technology still being actively developed. Neither of us know what the end results will be, but I put forth plausible reasoning to my speculation, if you have plausible reasoning why those things won’t come to pass I’m all ears. For instance, what is your reasoning for believing that AVs could never be fundamentally safer than human drivers who are frequently tired, angry, distracted, impaired, impatient, etc?
The difference is that Uber’s model of using an app to show you the route, give driver feedback, be able to report problems and monitor and track the driver, etc. is actually a huge improvement to both rider safety and experience compared to calling a cab company and then waiting who knows how long for someone to show up and hopefully bring you where you want to go.
Not saying that their model of gig workers, or dodging up front training is good, but they legitimately offered up a fundamentally better taxi experience than anything that came before, which I think encouraged regulators to really drag their feet on looking into them.